Determining the Disk Space of the SEAL indices¶
You can determine the required disk space of the SEAL indices in the Elasticsearch database with the following commands:
-
Linux:
curl -s -X GET "localhost:9200/seal*/_stats/store" -u elastic:elastic -H 'Content-Type: application/json' | jq '.indices | to_entries | map({(.key): .value.total.store.size_in_bytes}) | . + [{"Total": map(.[] | tonumber) | add}]' | jq -r '.[] | to_entries[] | "\(.key)\t\(.value)"' | column -t -s $'\t' -
Windows:
curl.exe -s -X GET "localhost:9200/seal*/_stats/store" -u elastic:elastic -H 'Content-Type: application/json' | jq '.indices | to_entries | map({(.key): .value.total.store.size_in_bytes}) | . + [{"Total": map(.[] | tonumber) | add}]' | jq -r '.[] | to_entries[] | "\(.key)\t\(.value)"' | column -t -s $'\t'
Example¶
Checking the disk space of the Elasticsearch database for the selected Indices:
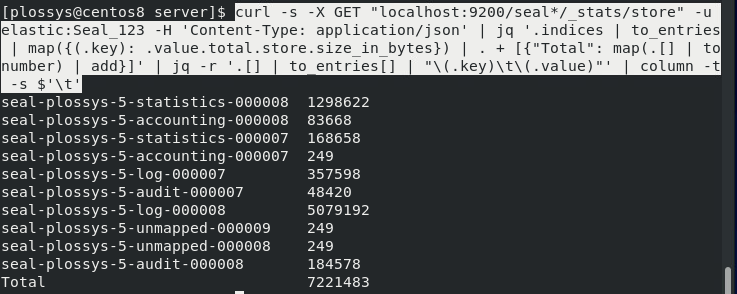
Hints on the Options¶
-
column:columnis a tool that converts thejqoutput into a table. -
jq:jqis a JSON-Parser that converts thecurloutput into a table. -
"localhost:9200":Adjust the
"localhost:9200"URL, if the Elasticsearch server runs on a different host or port. -
"seal*":"seal*"is the alias or index name. You can adjust it to your needs. -
"-u elastic:elastic":Depending on your security configuration, you can adjust
"-u elastic:elastic"as required or leave it out. -
self-signed certificates, etc.
In case of self-signed certificates, etc., use
-kor--insecure. -
indices the names of which do not start with
sealSeveral scripts create indices the names of which do not start with
seal. These indices require a separate retrieval.